-
Morphological analysis of oligomeric vs. fibrillar forms of α-synuclein aggregates with super-resolution BALM imaging
Hyun Huh, Jinwoo Lee, Hyung Jun Kim, Sungchul Hohng, Seong Keun Kim
Abstract
Application of BALM (binding activated localization microcopy) was shown to allow facile imaging of amyloid fibrils with a typical diameter of ∼14 nm FWHM. We also observed a twisted ribbon-like substructure of mutant amyloid fibrils and even what appear to be toxic amyloid oligomers with their characteristic morphological features consistent with TEM images. Use of an…
-
Increased PKMζ activity impedes lateral movement of GluA2-containing AMPA receptors
Nam-Kyung Yu, Heesoo Uhm, Jaehoon Shim, Jun-Hyeok Choi, Sangsu Bae, Todd Charlton Sacktor, Sungchul Hohng, Bong-Kiun Kaang
Abstract
Protein kinase M zeta (PKMζ), a constitutively active, atypical protein kinase C isoform, maintains a high level of expression in the brain after the induction of learning and long-term potentiation (LTP). Further, its overexpression enhances long-term memory and LTP. Thus, multiple lines of evidence suggest a significant role for persistently elevated PKMζ levels in long-term…
-
Ligand Recognition Mechanism of Thiamine Pyrophosphate Riboswitch Aptamer
Heesoo Uhm, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Riboswitches regulate gene expression by coupling ligand binding to a structural transition of the riboswitch, but the coupling mechanism is still controversial. We addressed this issue by characterizing both the ligand-free state of the Escherichia coli thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) riboswitch aptamer and its structural transition upon ligand binding using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)….
-
AUF1 facilitates microRNA-mediated gene silencing
Kyung-Won Min, Myung Hyun Jo, Soochul Shin, Sylvia Davila, Richard W Zealy, Soo Im Kang, Lawson T Lloyd, Sungchul Hohng, Je-Hyun Yoon
Abstract
Eukaryotic mRNA decay is tightly modulated by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). RBP AU-binding factor 1 (AUF1) has four isoforms resulting from alternative splicing and is critical for miRNA-mediated gene silencing with a distinct preference of target miRNAs. Previously, we have shown that AUF1 facilitates miRNA loading to Argonaute 2 (AGO2), the catalytic component…
-
NAP1L1 accelerates activation and decreases pausing to enhance nucleosome remodeling by CSB
Ju Yeon Lee, Robert J Lake, Jaewon Kirk, Vilhelm A Bohr, Hua-Ying Fan, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Cockayne syndrome protein B (CSB) belongs to the SWI2/SNF2 ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler family, and CSB is the only ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler essential for transcription-coupled nucleotide excision DNA repair. CSB alone remodels nucleosomes ∼10-fold slower than the ACF remodeling complex. Strikingly, NAP1-like histone chaperones interact with CSB and greatly enhance CSB-mediated chromatin remodeling. While chromatin remodeling…
-
Single-molecule fluorescence energy transfer assays for the characterization of reaction pathways of miRNA-argonaute complex
Myung Hyun Jo, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Argonaute proteins are key components of the microRNA-induced silencing complexes (miRISCs) that mediate the posttranscriptional gene silencing of microRNAs and small interfering RNA (siRNAs). The complex reaction mechanism of miRISC is expected to be characterized by tracing the reaction pathways of miRISC at the single-molecule level in real time. In this chapter, we describe single-molecule…
-
Single-molecule multicolor FRET assay for studying structural dynamics of biomolecules
S Lee, Y Jang, S-J Lee, S Hohng
Abstract
Over the last 2 decades, single-molecule Forster resonance energy transfer (FRET) has been widely used to address important questions in molecular biology. However, a conventional approach based on a single donor–acceptor pair is not powerful enough to study complex biological systems. To address this challenge, single-molecule multicolor FRET techniques have been developed. In this chapter,…
-
Active control of repetitive structural transitions between replication forks and holliday junctions by Werner syndrome helicase
Soochul Shin, Jinwoo Lee, Sangwoon Yoo, Tomasz Kulikowicz, Vilhelm A Bohr, Byungchan Ahn, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
The reactivation of stalled DNA replication via fork regression invokes Holliday junction formation, branch migration, and the recovery of the replication fork after DNA repair or error-free DNA synthesis. The coordination mechanism for these DNA structural transitions by molecular motors, however, remains unclear. Here we perform single-molecule fluorescence experiments with Werner syndrome protein (WRN) and…
-
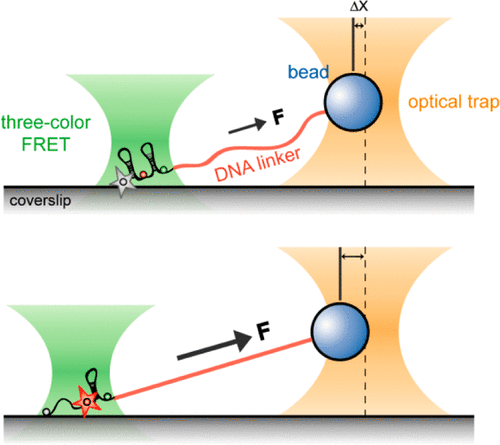
Single‐Molecule FRET Combined with Magnetic Tweezers at Low Force Regime
Heesoo Uhm, Sangsu Bae, Mina Lee, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
We present the development and characterization of a single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscope combined with magnetic tweezers (MT) for studying mechano-sensitive biochemical reactions. The setup integrates objective-type total internal reflection FRET microscopy with a compact MT system. A novel symmetry recognition method was developed for x-y positioning of magnetic beads, achieving positioning accuracy…
-
Single-molecule fluorescence measurements reveal the reaction mechanisms of the core-RISC, composed of human Argonaute 2 and a guide RNA
Myung Hyun Jo, Ji-Joon Song, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
In eukaryotes, small RNAs play important roles in both gene regulation and resistance to viral infection. Argonaute proteins have been identified as a key component of the effector complexes of various RNA-silencing pathways, but the mechanistic roles of Argonaute proteins in these pathways are not clearly understood. To address this question, we performed single-molecule fluorescence…
-
Structure of human DROSHA
S Chul Kwon, Tuan Anh Nguyen, Yeon-Gil Choi, Myung Hyun Jo, Sungchul Hohng, V Narry Kim, Jae-Sung Woo
Abstract
MicroRNA maturation is initiated by RNase III DROSHA that cleaves the stem loop of primary microRNA. DROSHA functions together with its cofactor DGCR8 in a heterotrimeric complex known as Microprocessor. Here, we report the X-ray structure of DROSHA in complex with the C-terminal helix of DGCR8. We find that DROSHA contains two DGCR8-binding sites, one…
-
AUF1 promotes let-7b loading on Argonaute 2
Je-Hyun Yoon, Myung Hyun Jo, Elizabeth JF White, Supriyo De, Markus Hafner, Beth E Zucconi, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jennifer L Martindale, Xiaoling Yang, William H Wood, Yu Mi Shin, Ji-Joon Song, Thomas Tuschl, Kevin G Becker, Gerald M Wilson, Sungchul Hohng, Myriam Gorospe
Abstract
Eukaryotic gene expression is tightly regulated post-transcriptionally by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and microRNAs. The RBP AU-rich-binding factor 1 (AUF1) isoform p37 was found to have high affinity for the microRNA let-7b in vitro (Kd = ∼6 nM) in cells. Ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation, in vitro association, and single-molecule-binding analyses revealed that AUF1 promoted let-7b loading onto Argonaute…
-
Human Argonaute 2 has diverse reaction pathways on target RNAs
Myung Hyun Jo, Soochul Shin, Seung-Ryoung Jung, Eunji Kim, Ji-Joon Song, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Argonaute is a key enzyme of various RNA silencing pathways. We use single-molecule fluorescence measurements to characterize the reaction mechanisms of the core-RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) composed of human Argonaute 2 and a small RNA. We found that target binding of core-RISC starts at the seed region, resulting in four distinct reaction pathways: target cleavage,…
-
Functional anatomy of the human microprocessor
Tuan Anh Nguyen, Myung Hyun Jo, Yeon-Gil Choi, Joha Park, S Chul Kwon, Sungchul Hohng, V Narry Kim, Jae-Sung Woo
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) maturation is initiated by Microprocessor composed of RNase III DROSHA and its cofactor DGCR8, whose fidelity is critical for generation of functional miRNAs. To understand how Microprocessor recognizes pri-miRNAs, we here reconstitute human Microprocessor with purified recombinant proteins. We find that Microprocessor is an ∼364 kDa heterotrimeric complex of one DROSHA and two…
-
Dicer Nuclease‐Promoted Production of Let7a‐1 MicroRNA Is Enhanced in the Presence of Tryptophan‐Containing Amphiphilic Peptides
Soonsil Hyun, Areum Han, Myung Hyun Jo, Sungchul Hohng, Jaehoon Yu
Abstract
Accelerate let7a-1 production: Dicer nuclease cleaves endogenous pre-miRNA into mature miRNA without substrate specificity. Transforming nonspecific Dicer into a substrate-specific endonuclease could regulate miRNA production. We report peptides that bind pre-let7a-1 thus improving mature let7a-1 production by Dicer-promoted selective cleavage of pre-let7a-1.