-
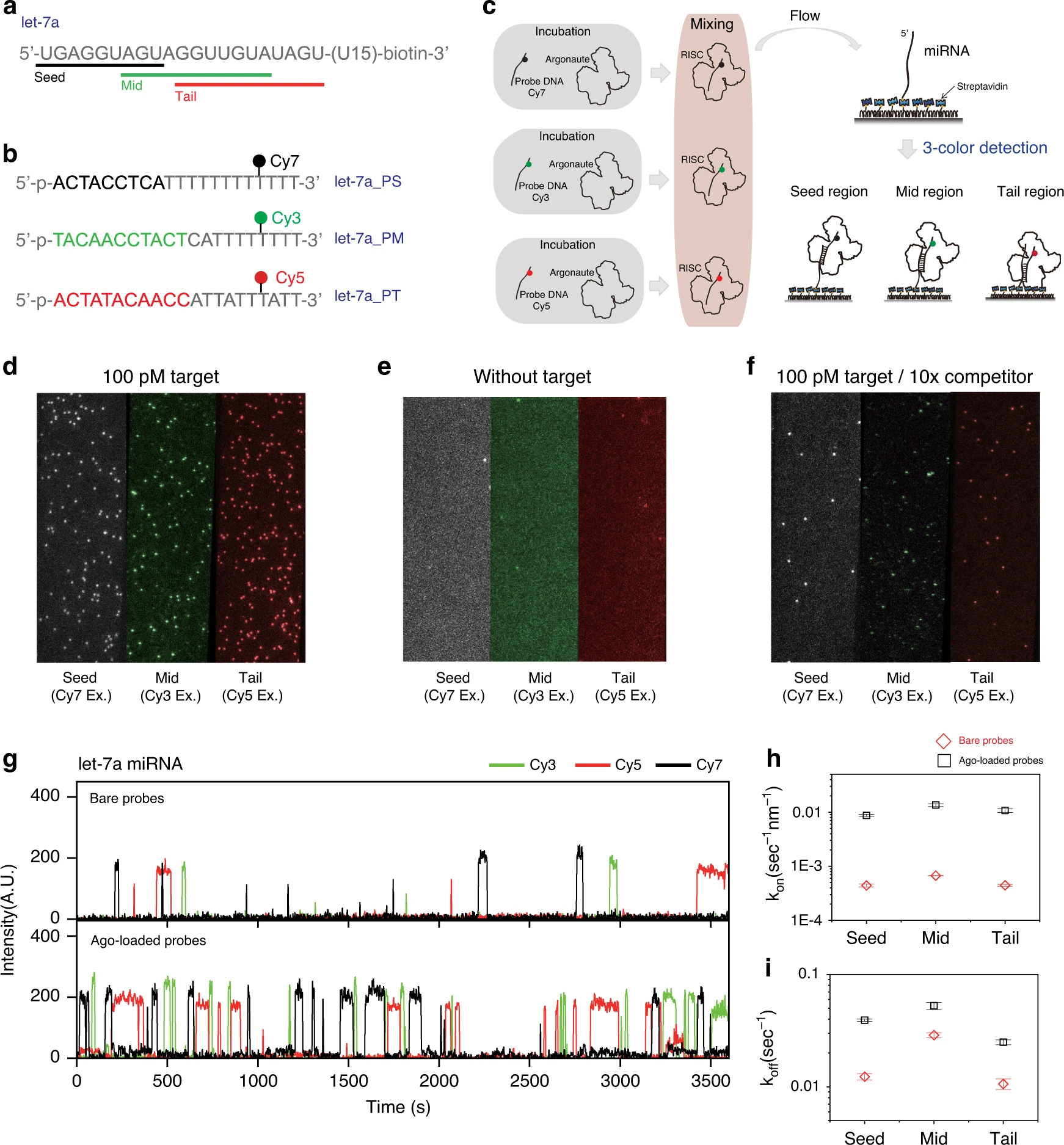
Quantification of purified endogenous miRNAs with high sensitivity and specificity
Soochul Shin, Yoonseok Jung, Heesoo Uhm, Minseok Song, Soomin Son, Jiyoung Goo, Cherlhyun Jeong, Ji-Joon Song, V Narry Kim, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short (19–24 nt) non-coding RNAs that suppress the expression of protein coding genes at the post-transcriptional level. Differential expression profiles of miRNAs across a range of diseases have emerged as powerful biomarkers, making a reliable yet rapid profiling technique for miRNAs potentially essential in clinics. Here, we report an amplification-free multi-color single-molecule…
-
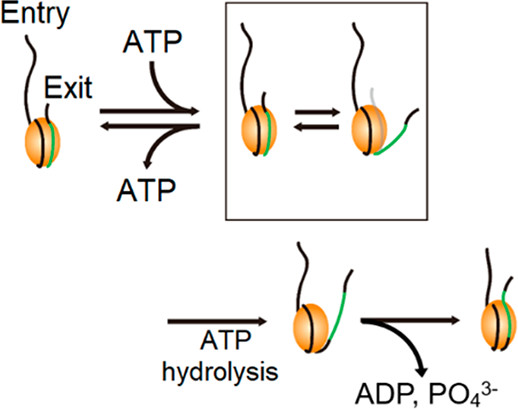
Yeast Chd1p Unwraps the Exit Side DNA upon ATP Binding to Facilitate the Nucleosome Translocation Occurring upon ATP Hydrolysis
Jaewon Kirk, Ju Yeon Lee, Yejin Lee, Chanshin Kang, Soochul Shin, Eunhye Lee, Ji-Joon Song, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1 (CHD1) remodels chromatin by translocating nucleosomes along DNA, but its mechanism remains poorly understood. We use single-molecule fluorescence experiments to clarify the mechanism by which yeast CHD1 (Chd1p) remodels nucleosomes. We find that binding of ATP to Chd1p induces transient unwrapping of the DNA on the exit side of the nucleosome, facilitating…
-
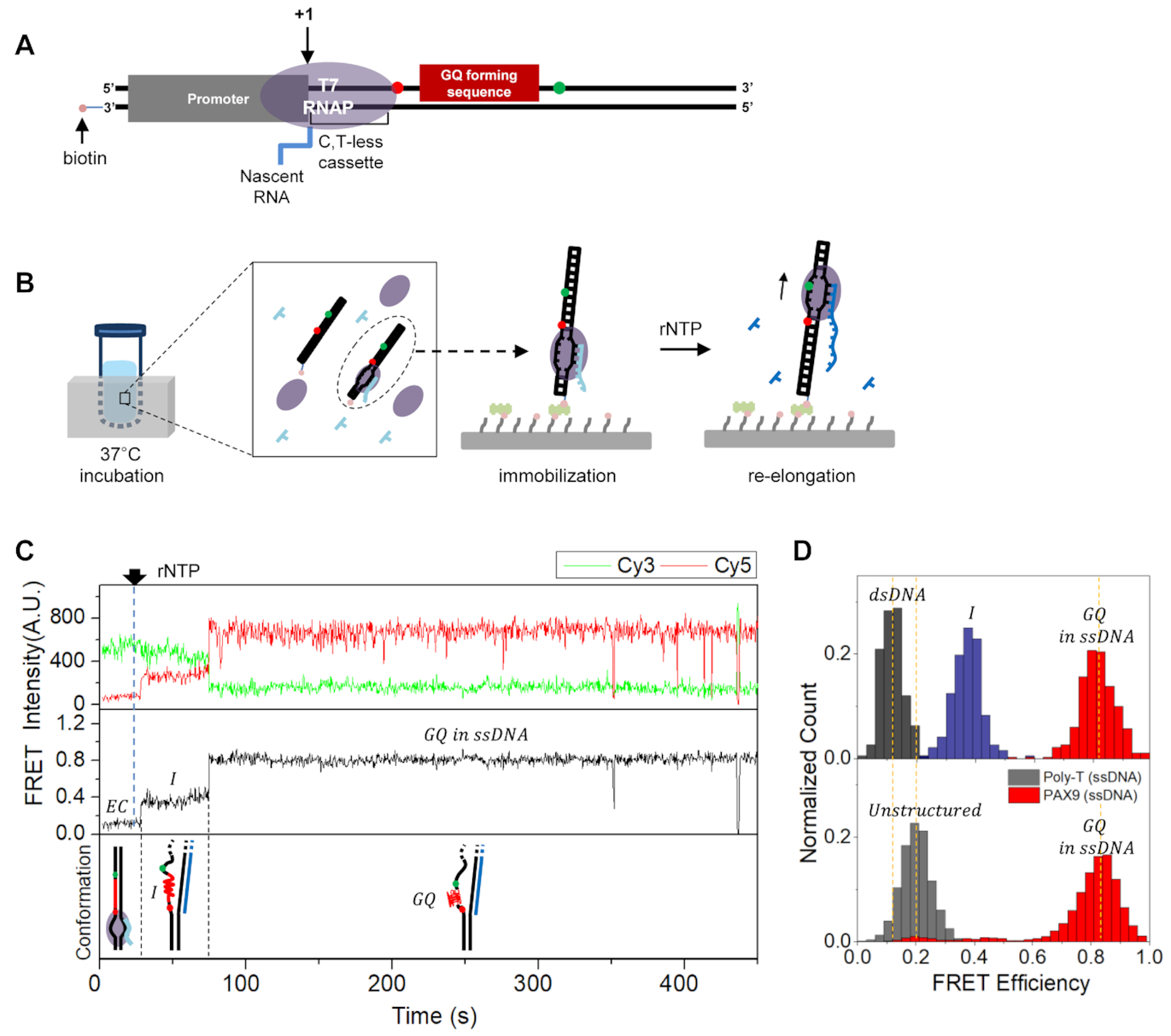
Single-molecule fluorescence studies on cotranscriptional G-quadruplex formation coupled with R-loop formation
Gunhyoung Lim, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
G-quadruplex (GQ) is formed at various regions of DNA, including telomeres of chromosomes and regulatory regions of oncogenes. Since GQ is important in both gene regulation and genome instability, the biological and medical implications of this abnormal DNA structure have been intensively studied. Its formation mechanisms, however, are not clearly understood yet. We report single-molecule…
-
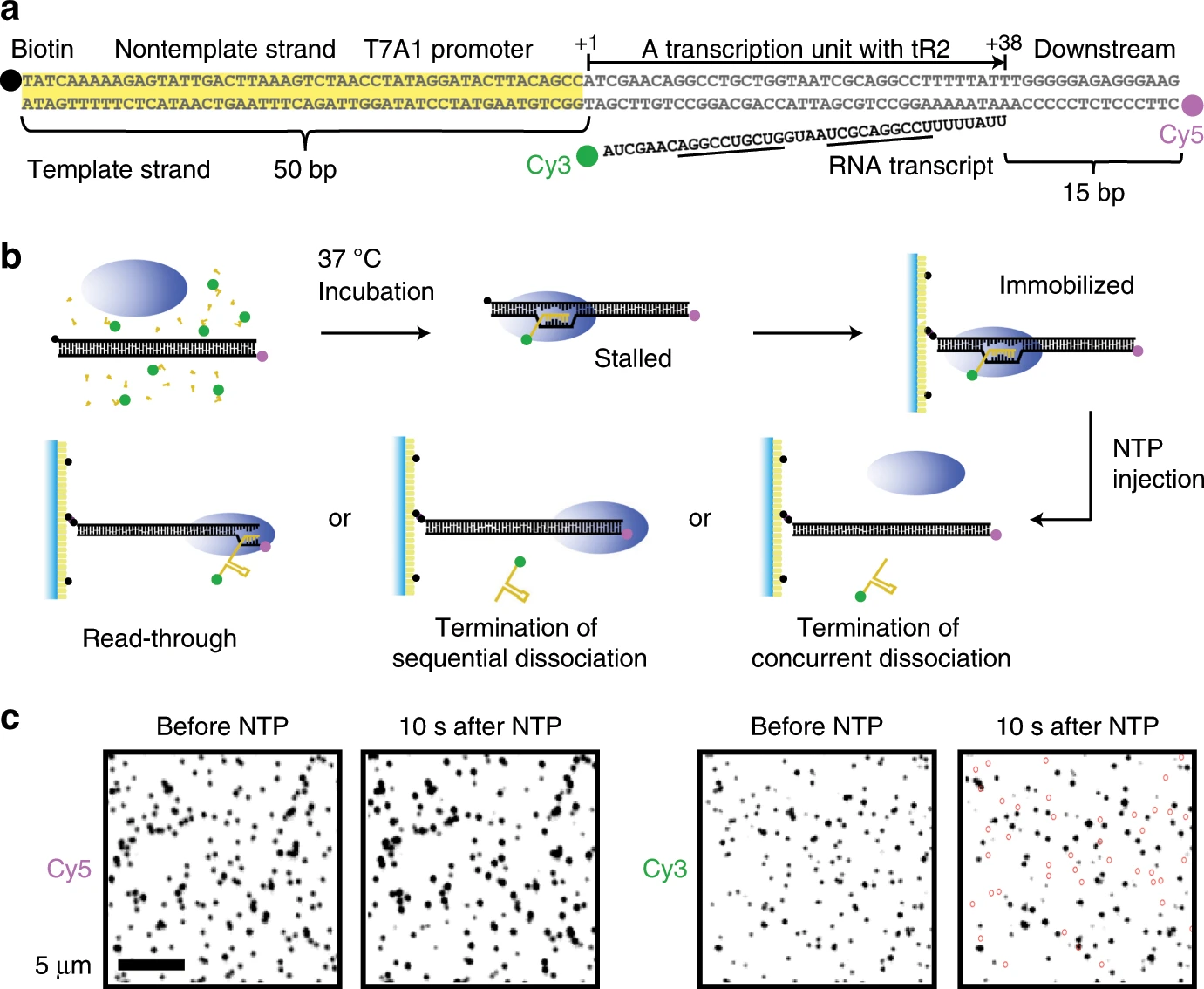
Transcription reinitiation by recycling RNA polymerase that diffuses on DNA after releasing terminated RNA
Wooyoung Kang, Kook Sun Ha, Heesoo Uhm, Kyuhyong Park, Ja Yil Lee, Sungchul Hohng, Changwon Kang
Abstract
Despite extensive studies on transcription mechanisms, it is unknown how termination complexes are disassembled, especially in what order the essential components dissociate. Our single-molecule fluorescence study unveils that RNA transcript release precedes RNA polymerase (RNAP) dissociation from the DNA template much more often than their concurrent dissociations in intrinsic termination of bacterial transcription. As termination…
-
Single-molecule FRET assay for studying cotranscriptional RNA folding
Heesoo Uhm, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Cotranscriptional RNA folding plays important roles in gene regulation steps such as splicing, transcription termination, and translation initiation. Progression of our understanding of cotranscriptional RNA folding mechanisms is still retarded by the lacking of experimental tools to study the kinetics of cotranscriptional RNA folding properly. In this chapter, we describe fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)…
-
ATAD5 promotes replication restart by regulating RAD51 and PCNA in response to replication stress
Su Hyung Park, Nalae Kang, Eunho Song, Minwoo Wie, Eun A Lee, Sunyoung Hwang, Deokjae Lee, Jae Sun Ra, In Bae Park, Jieun Park, Sukhyun Kang, Jun Hong Park, Sungchul Hohng, Kyoo-young Lee, Kyungjae Myung
Abstract
Maintaining stability of replication forks is important for genomic integrity. However, it is not clear how replisome proteins contribute to fork stability under replication stress. Here, we report that ATAD5, a PCNA unloader, plays multiple functions at stalled forks including promoting its restart. ATAD5 depletion increases genomic instability upon hydroxyurea treatment in cultured cells and…
-
Structural basis of recognition and destabilization of the histone H2B ubiquitinated nucleosome by the DOT1L histone H3 Lys79 methyltransferase
Seongmin Jang, Chanshin Kang, Han-Sol Yang, Taeyang Jung, Hans Hebert, Ka Young Chung, Seung Joong Kim, Sungchul Hohng, Ji-Joon Song
Abstract
DOT1L is a histone H3 Lys79 methyltransferase whose activity is stimulated by histone H2B Lys120 ubiquitination, suggesting cross-talk between histone H3 methylation and H2B ubiquitination. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of DOT1L complexes with unmodified or H2B ubiquitinated nucleosomes, showing that DOT1L recognizes H2B ubiquitin and the H2A/H2B acidic patch through a C-terminal hydrophobic helix…
-
Accelerated fret-paint microscopy
Jongjin Lee, Sangjun Park, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Recent development of FRET-PAINT microscopy significantly improved the imaging speed of DNA-PAINT, the previously reported super-resolution fluorescence microscopy with no photobleaching problem. Here we try to achieve the ultimate speed limit of FRET-PAINT by optimizing the camera speed, dissociation rate of DNA probes, and bleed-through of the donor signal to the acceptor channel, and further…
-
Multiple RPAs make WRN syndrome protein a superhelicase
Mina Lee, Soochul Shin, Heesoo Uhm, Heesun Hong, Jaewon Kirk, Kwangbeom Hyun, Tomasz Kulikowicz, Jaehoon Kim, Byungchan Ahn, Vilhelm A Bohr, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
RPA is known to stimulate the helicase activity of Werner syndrome protein (WRN), but the exact stimulation mechanism is not understood. We use single-molecule FRET and magnetic tweezers to investigate the helicase activity of WRN and its stimulation by RPA. We show that WRN alone is a weak helicase which repetitively unwind just a few…
-
ATP binding to Rad5 initiates replication fork reversal by inducing the unwinding of the leading arm and the formation of the Holliday junction
Soochul Shin, Kwangbeom Hyun, Jaehoon Kim, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Replication fork reversal is one of the major pathways for reactivating stalled DNA replication. Many enzymes with replication fork reversal activity have DNA-unwinding activity as well, but none of the fork reversal enzymes in the SWI/SNF family shows a separate DNA-unwinding activity, raising the question of how they initiate the remodeling process. Here, we found…
-
Real‐Time Monitoring of the Binding/Dissociation and Redox States of a Single Transition Metal Ions
Seung‐Ryoung Jung, Sang‐Wook Lee, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between organic fluorophores is conventionally used to monitor binding/dissociation and conformational change of macromolecules. Here we use FRET between a cyanine dye and single transition metal ions (tmFRET) to monitor the binding/dissociation of transition metal ions to a synthetic polypeptide, and show that different transition metal ion species can be…
-
Superresolution fluorescence microscopy for 3D reconstruction of thick samples
Sangjun Park, Wooyoung Kang, Yeong-Dae Kwon, Jaehoon Shim, Siyong Kim, Bong-Kiun Kaang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of thick samples using superresolution fluorescence microscopy remains challenging due to high level of background noise and fast photobleaching of fluorescence probes. We develop superresolution fluorescence microscopy that can reconstruct 3D structures of thick samples with both high localization accuracy and no photobleaching problem. The background noise is reduced by optically sectioning…
-
Single-molecule FRET studies on the cotranscriptional folding of a thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch
Heesoo Uhm, Wooyoung Kang, Kook Sun Ha, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Because RNAs fold as they are being synthesized, their transcription rate can affect their folding. Here, we report the results of single-molecule fluorescence studies that characterize the ligand-dependent cotranscriptional folding of the Escherichia coli thiM riboswitch that regulates translation. We found that the riboswitch aptamer folds into the “off” conformation independent of its ligand, but…
-
Mechanisms of the Binding/Dissociation Acceleration of the Target–Guide Interaction by Thermus thermophilus Argonaute
Seung‐Ryoung Jung, Eunji Kim, Soochul Shin, Ji‐Joon Song, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Prokaryotic Argonaute facilitates the target recognition process by the guide strand via a still unknown mechanism. Using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer and systematic mutagenesis of Thermus thermophilus Argonaute and guide-target base pairing, we study the kinetic roles of various structural features of guide strand in the prokaryotic Argonaute. We reveal that the 5′-end anchoring…
-
Accelerated super-resolution imaging with FRET-PAINT
Jongjin Lee, Sangjun Park, Wooyoung Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy in the current form is hard to be used to image the neural connectivity of thick tissue samples due to problems such as slow imaging speed, severe photobleaching of fluorescent probes, and high background noise. Recently developed DNA-PAINT solved the photobleaching problem, but its imaging speed is extremely low. We report accelerated…