-
Analytical techniques for nucleic acid and protein detection with single-molecule sensitivity
Soochul Shin, Juyoung Kim, Eunho Song, Sun Han, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Nucleic acids and proteins serve as crucial biomarkers used in the diagnosis, prognosis and therapy monitoring across various diseases. Traditionally, these biomarkers are identified at an ensemble level following the amplification of target or signaling molecules. However, these methods have limitations in addressing contemporary challenges in molecular diagnostics, such as low sensitivity, specificity, throughput and…
-
Kinesin-like protein KIF18A is required for faithful coordination of chromosome congression with cytokinesis
Su Hyun Lee, Mi-Sun Kwon, Taerim Lee, Sungchul Hohng, Hyunsook Lee
Abstract
The maintenance of genetic integrity in proliferating cells requires the coordinated regulation of DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cytokinetic abscission. Chromosome-microtubule interactions regulate mitosis, while interactions between the actin cytoskeleton and Myosin IIA dictate cytokinetic abscission. This process, crucial for the equal distribution of the duplicated genome into two daughter cells, occurs perpendicular to the…
-
Single-mode termination of phage transcriptions, disclosing bacterial adaptation for facilitated reinitiations
Eunho Song, Sun Han, Heesoo Uhm, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Bacterial and bacteriophage RNA polymerases (RNAPs) have divergently evolved and share the RNA hairpin-dependent intrinsic termination of transcription. Here, we examined phage T7, T3 and SP6 RNAP terminations utilizing the single-molecule fluorescence assays we had developed for bacterial terminations. We discovered the phage termination mode or outcome is virtually single with decomposing termination. Therein, RNAP…
-
Compatibility of termination mechanisms in bacterial transcription with inference on eukaryotic models
Eunho Song, Sun Han, Sungchul Hohng, Changwon Kang
Abstract
Transcription termination has evolved to proceed through diverse mechanisms. For several classes of terminators, multiple models have been debatably proposed. Recent single-molecule studies on bacterial terminators have resolved several long-standing controversies. First, termination mode or outcome is twofold rather than single. RNA is released alone before DNA or together with DNA from RNA polymerase (RNAP),…
-
Mature microRNA-binding protein QKI promotes microRNA-mediated gene silencing
Kyung-Won Min, Myung Hyun Jo, Minseok Song, Ji Won Lee, Min Ji Shim, Kyungmin Kim, Hyun Bong Park, Shinwon Ha, Hyejin Mun, Ahsan Polash, Markus Hafner, Jung-Hyun Cho, Dongsan Kim, Ji-Hoon Jeong, Seungbeom Ko, Sungchul Hohng, Sung-Ung Kang, Je-Hyun Yoon
Abstract
Although Argonaute (AGO) proteins have been the focus of microRNA (miRNA) studies, we observed AGO-free mature miRNAs directly interacting with RNA-binding proteins, implying the sophisticated nature of fine-tuning gene regulation by miRNAs. To investigate microRNA-binding proteins (miRBPs) globally, we analyzed PAR-CLIP data sets to identify RBP quaking (QKI) as a novel miRBP for let-7b. Potential…
-
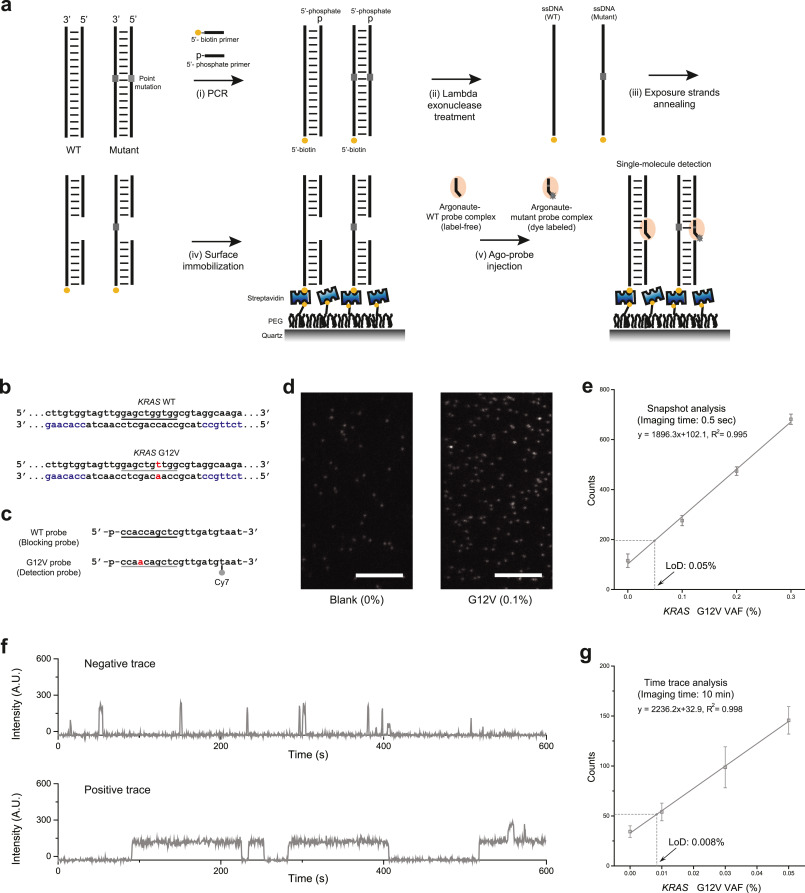
Fast, sensitive, and specific multiplexed single-molecule detection of circulating tumor DNA
Soochul Shin, Sun Han, Juyoung Kim, Yumi Shin, Ji-Joon Song, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis has emerged as a highly promising non-invasive assay for detection and monitoring of cancer. However, identification of multiple point-mutant ctDNAs, particularly at extremely low frequencies in early cancer stages, remains a significant challenge. To address this issue, we present a multiplexed ctDNA detection technique, SIMUL (single-molecule detection of multiple low-frequency…
-
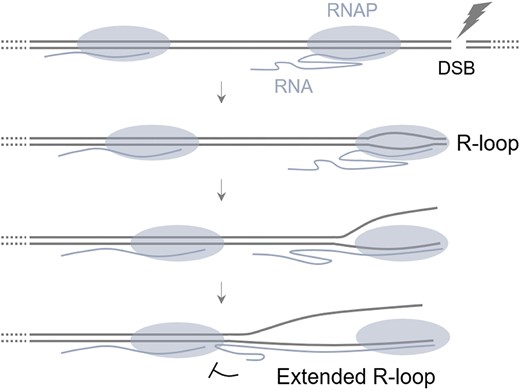
Translocating RNA polymerase generates R-loops at DNA double-strand breaks without any additional factors
Gunhyoung Lim, Seungha Hwang, Kilwon Yu, Jin Young Kang, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Translocating RNA polymerase generates R-loops at DNA double-strand breaks without any additional factors
-
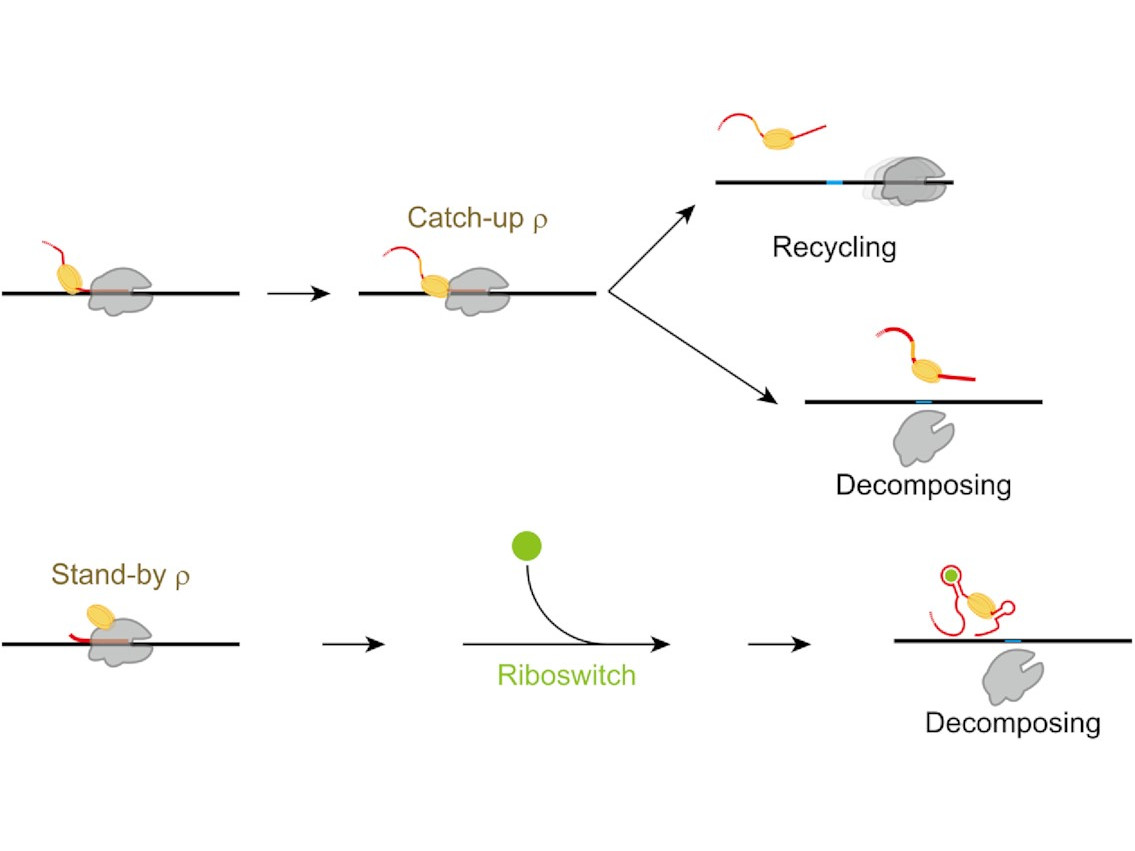
Transcriptional pause extension benefits the stand-by rather than catch-up Rho-dependent termination
Eunho Song, Seungha Hwang, Palinda Ruvan Munasingha, Yeon-Soo Seo, Jin Young Kang, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Transcriptional pause is essential for all types of termination. In this single-molecule study on bacterial Rho factor-dependent terminators, we confirm that the three Rho-dependent termination routes operate compatibly together in a single terminator, and discover that their termination efficiencies depend on the terminational pauses in unexpected ways. Evidently, the most abundant route is that Rho…
-
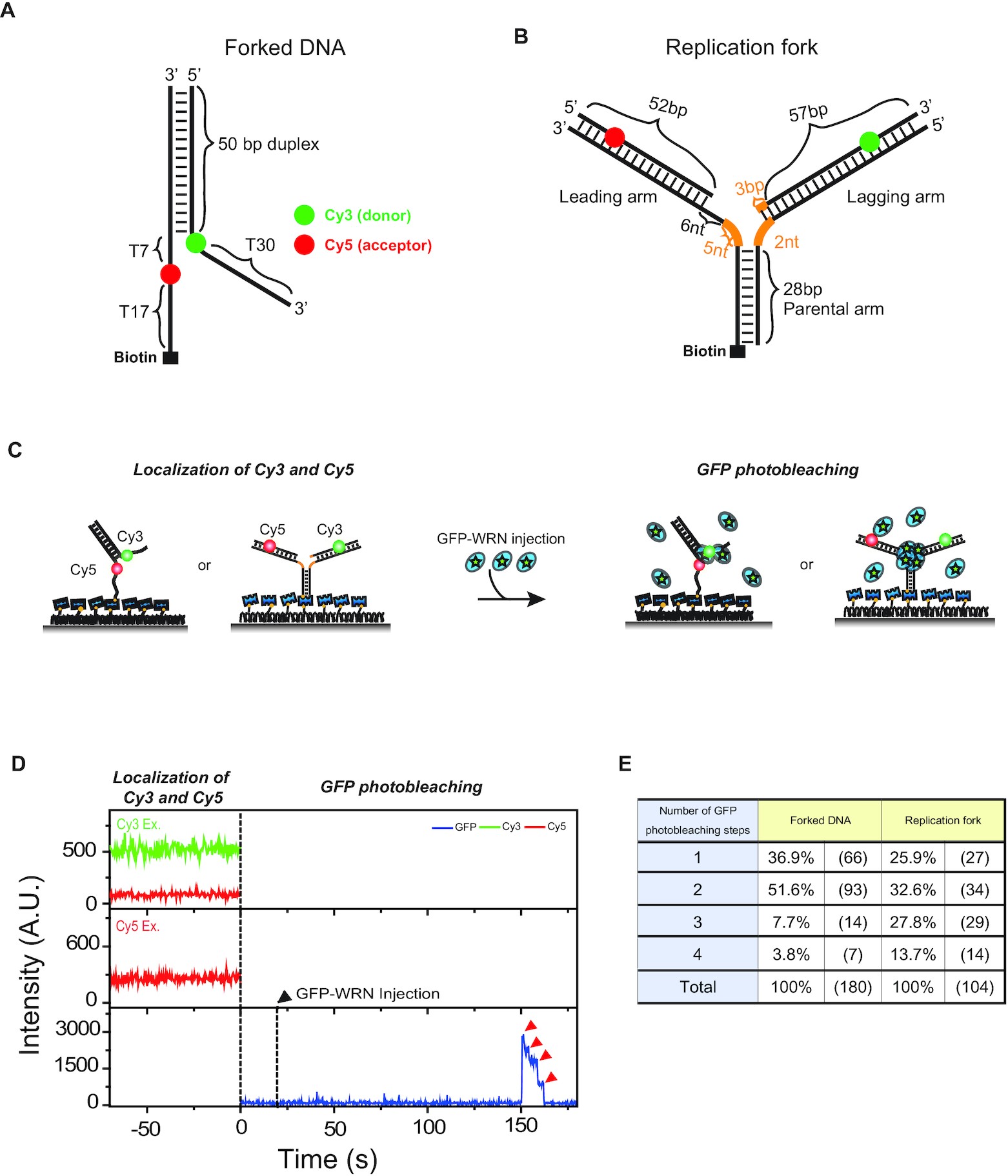
Werner syndrome protein works as a dimer for unwinding and replication fork regression
Soochul Shin, Kwangbeom Hyun, Jinwoo Lee, Dongwon Joo, Tomasz Kulikowicz, Vilhelm A Bohr, Jaehoon Kim, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
The determination of the oligomeric state of functional enzymes is essential for the mechanistic understanding of their catalytic activities. RecQ helicases have diverse biochemical activities, but it is still unclear how their activities are related to their oligomeric states. We use single-molecule multi-color fluorescence imaging to determine the oligomeric states of Werner syndrome protein (WRN)…
-
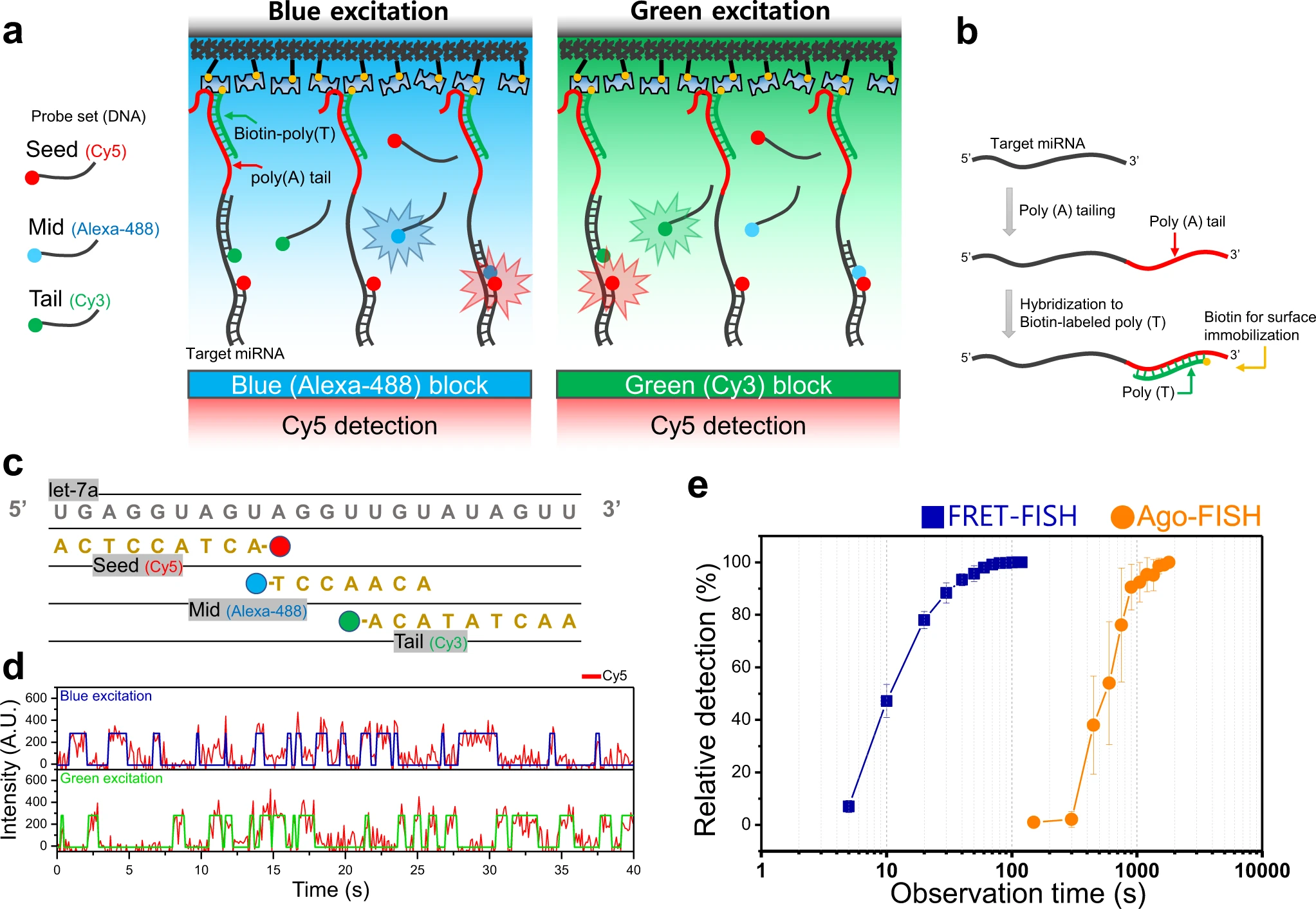
Rapid quantification of miRNAs using dynamic FRET-FISH
Juyoung Kim, Chanshin Kang, Soochul Shin, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short regulatory RNAs that control gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Various miRNAs playing important roles in cancer development are emerging as promising diagnostic biomarkers for early cancer detection. Accurate miRNA detection, however, remains challenging because they are small and highly homologous. Recently developed miRNA detection techniques based on single-molecule imaging enabled…
-
Rho-dependent transcription termination proceeds via three routes
Eunho Song, Heesoo Uhm, Palinda Ruvan Munasingha, Seungha Hwang, Yeon-Soo Seo, Jin Young Kang, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Rho is a general transcription termination factor in bacteria, but many aspects of its mechanism of action are unclear. Diverse models have been proposed for the initial interaction between the RNA polymerase (RNAP) and Rho (catch-up and stand-by pre-terminational models); for the terminational release of the RNA transcript (RNA shearing, RNAP hyper-translocation or displacing, and…
-
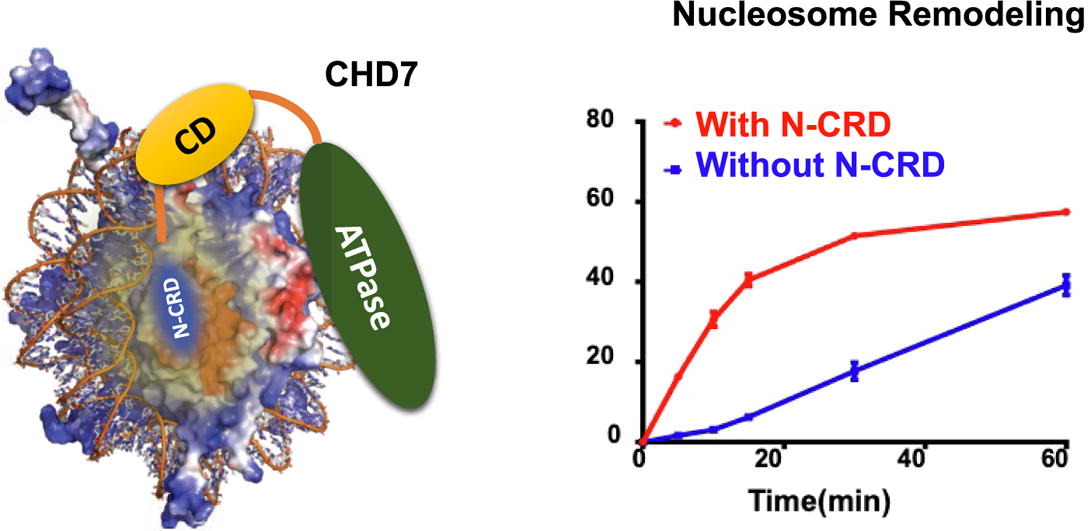
A Novel N-terminal Region to Chromodomain in CHD7 is Required for the Efficient Remodeling Activity
Eunhye Lee, Chanshin Kang, Pasi Purhonen, Hans Hebert, Karim Bouazoune, Sungchul Hohng, Ji-Joon Song
Abstract
Chromodomain-Helicase DNA binding protein 7 (CHD7) is an ATP dependent chromatin remodeler involved in maintaining open chromatin structure. Mutations of CHD7 gene causes multiple developmental disorders, notably CHARGE syndrome. However, there is not much known about the molecular mechanism by which CHD7 remodels nucleosomes. Here, we performed biochemical and biophysical analysis on CHD7 chromatin remodeler…
-
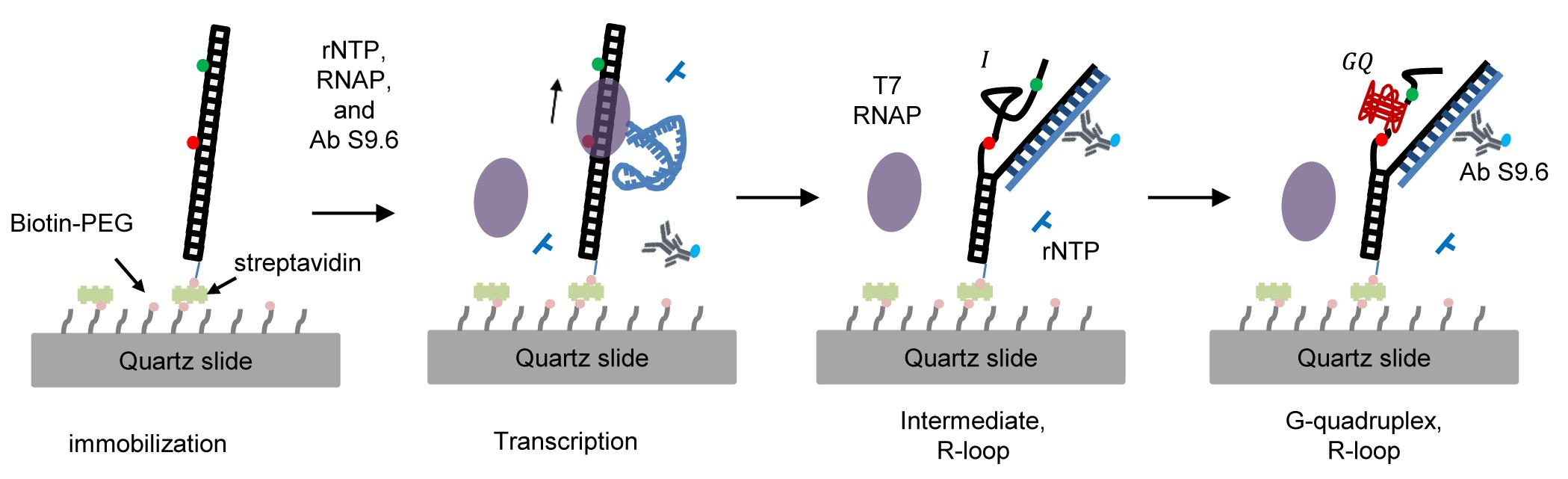
Single-molecule Fluorescence Technique to Monitor the Co-transcriptional Formation of G-quadruplex and R-loop Structures
Gunhyoung Lim, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
G-quadruplexes (GQ) and R-loops are non-canonical nucleic acid structures related to gene regulation and genome instability that can be formed during transcription; however, their formation mechanisms remain elusive. To address this question, we developed a single-molecule fluorescence technique to monitor the formation of G-quadruplex and R-loop structures during transcription. Using this technique, we found that…
-
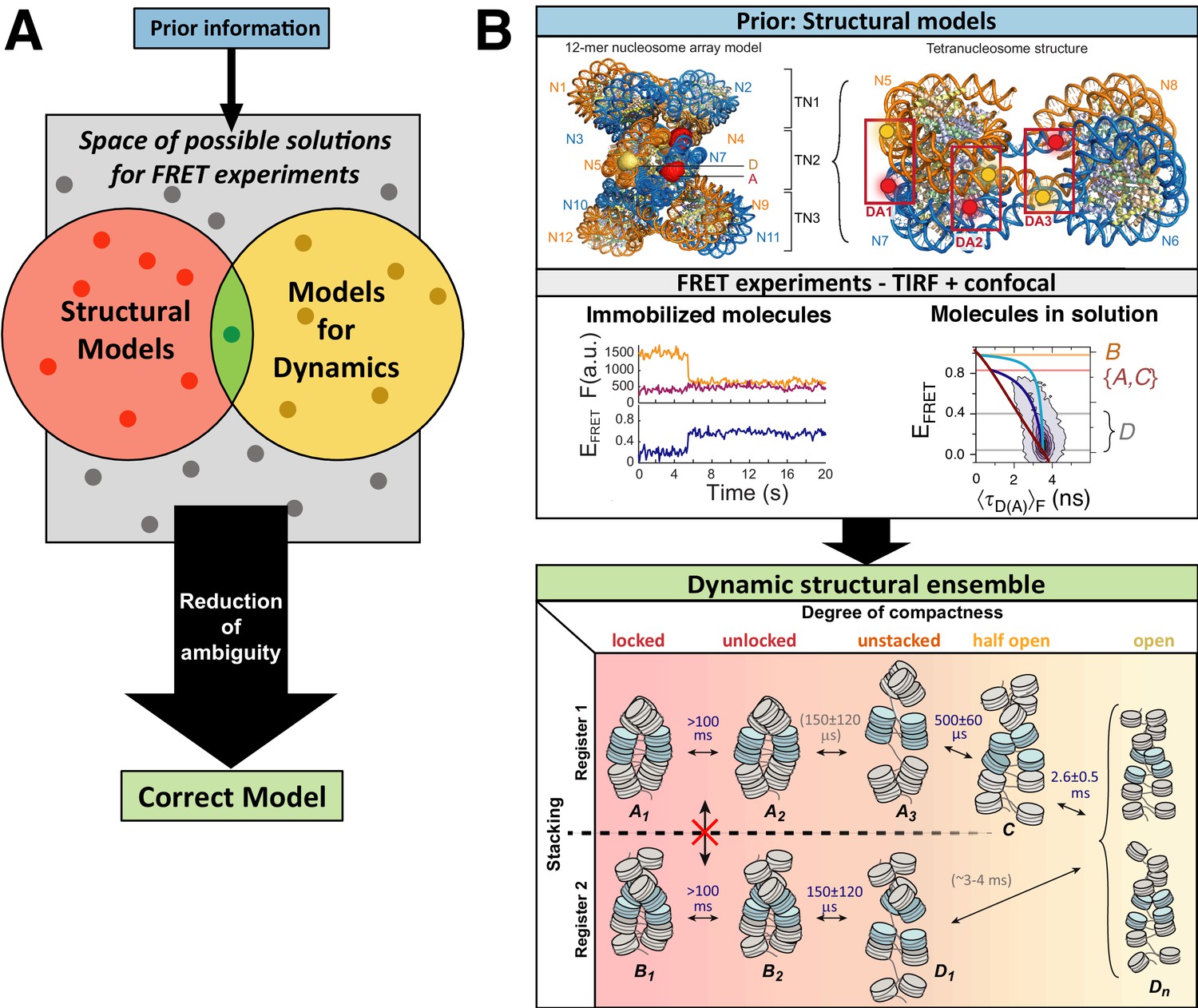
FRET-based dynamic structural biology: Challenges, perspectives and an appeal for open-science practices
Eitan Lerner, Anders Barth, Jelle Hendrix, Benjamin Ambrose, Victoria Birkedal, Scott C Blanchard, Richard Börner, Hoi Sung Chung, Thorben Cordes, Timothy D Craggs, Ashok A Deniz, Jiajie Diao, Jingyi Fei, Ruben L Gonzalez, Irina V Gopich, Taekjip Ha, Christian A Hanke, Gilad Haran, Nikos S Hatzakis, Sungchul Hohng, Seok-Cheol Hong, Thorsten Hugel, Antonino Ingargiola, Chirlmin Joo, Achillefs N Kapanidis, Harold D Kim, Ted Laurence, Nam Ki Lee, Tae-Hee Lee, Edward A Lemke, Emmanuel Margeat, Jens Michaelis, Xavier Michalet, Sua Myong, Daniel Nettels, Thomas-Otavio Peulen, Evelyn Ploetz, Yair Razvag, Nicole C Robb, Benjamin Schuler, Hamid Soleimaninejad, Chun Tang, Reza Vafabakhsh, Don C Lamb, Claus AM Seidel, Shimon Weiss
Abstract
Single-molecule FRET (smFRET) has become a mainstream technique for studying biomolecular structural dynamics. The rapid and wide adoption of smFRET experiments by an ever-increasing number of groups has generated significant progress in sample preparation, measurement procedures, data analysis, algorithms and documentation. Several labs that employ smFRET approaches have joined forces to inform the smFRET community…
-
Hopping and flipping of RNA polymerase on DNA during recycling for reinitiation after intrinsic termination in bacterial transcription
Wooyoung Kang, Seungha Hwang, Jin Young Kang, Changwon Kang, Sungchul Hohng
Abstract
Two different molecular mechanisms, sliding and hopping, are employed by DNA-binding proteins for their one-dimensional facilitated diffusion on nonspecific DNA regions until reaching their specific target sequences. While it has been controversial whether RNA polymerases (RNAPs) use one-dimensional diffusion in targeting their promoters for transcription initiation, two recent single-molecule studies discovered that post-terminational RNAPs use…